What is Client-Server Architecture ?
The client-server architecture or model is an application network separating tasks between clients and servers that are either within the same system or need to communicate over a network. In order to access the service provided by the server, the server-client sends the request to another program, which runs a few programs that distribute work among the clients & share resources with them.
A client-server relationship corresponds to the request-response pattern and should adhere to a standard communications protocol that defines the language and rules used for the communications. The client-server communication adheres to the TCP protocol suite.
The Internet Protocol is a connectionless protocol, which means that each packet traveling on the Internet is an independent piece of data, unconnected to any other packet.
How Does Client-Server Architecture Work?
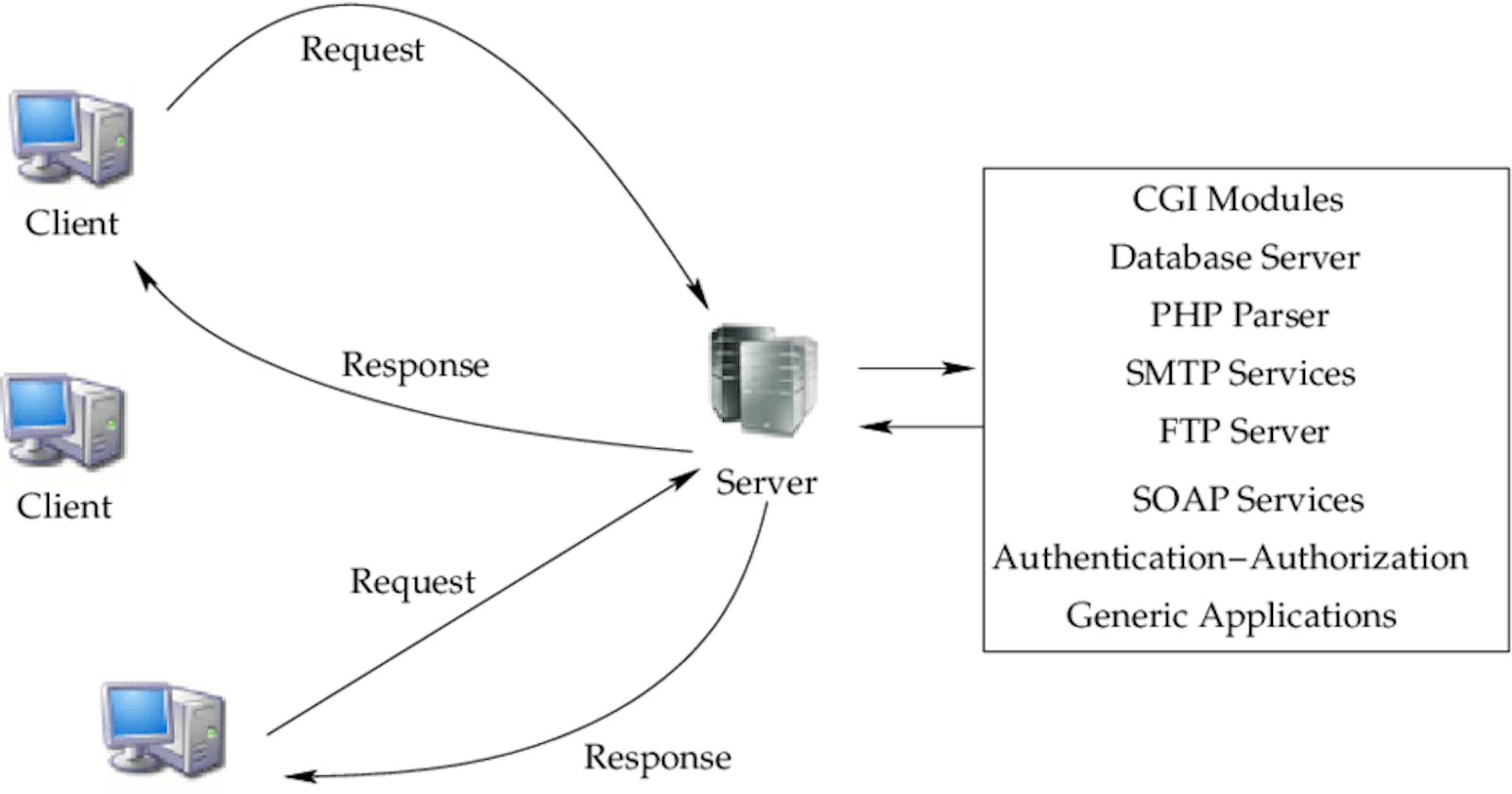
We already have studied what is the client and what is the server. Now let’s understand the working of this architecture.

In the above image, If any client wants some data with any server then it first asks for the IP address for the particular server from the DNS (Domain name System). The DNS server responds with the IP Address.
To that IP Address, the client sends the request to the particular server with the port number that is specified to the particular application, and then the server responds. The response message receives by the client and based on the port number, the response packet is consumed by the application to which it belongs.
Here at a very high level, the communication between the client and server happens over the HTTP packets.
Advantages of Client-Server Architecture
Management is Easy – It is rather easy to manage the files because they are all stored on one server. Client-server networks have the best management to track and find records of required files.
Easily Accessible – Clients can log into the system regardless of their location or their platform of choice, allowing each employee to access their corporate information without having to use a terminal mode or a processor.
Servers are Scalable – A client-server network is highly scalable. Whenever the user needs, they can add more resources such as clients and servers, thus increasing the size of the server without any interruption. Due to the fact that the server is centralized, permission to network resources is not an issue, so very few staff members are required for configurations even if the size increases.
Centralized Control – Client-server networks have the advantage of centralized control since all information is stored in a single location. Since the network administrator has full control over management and administration, this is especially beneficial. As a result, any problems that arise throughout the entire network can be solved from one central location. As a result, it has also become much easier to update data and resources.
Security – Due to its centralized architecture, client-server networks protect data well. A single backup can be used to recover all of the files if the data are lost, such as imposing credentials like username and passwords. Another method of enforcing access controls is imposing credentials like username and password.
Disadvantages of Client-Server Architecture
Less Robust – Due to client-server networks’ centralized nature, in case the main server undergoes failure or interference, the entire network will be interrupted. Thus, client-server networks are less robust.
Requires Regular Maintenance – Servers will run continuously on the network. This means they must be properly maintained. If there are any problems, they should be fixed immediately. A network manager should be appointed to maintain the server.
Requires Cost – In a client-server network, the cost of setting up and maintaining the server is usually very high, just as it is on the network operations. Because the networks are powerful, they can be expensive to purchase. Thus, not all users will be able to take advantage of them.
Network Congestion – If too many clients access a single server, it may result in crashes or slowed-down connectivity. An overloaded server presents many problems when accessing information.